I recently moved one of my WP websites to a new host. The old host was Japanese and the new is American. But the site’s URL remains the same. No one would ever notice the change until he checks the hosting provider. Migrating a WP website from one host to another with the same domain name is indeed quite possible. It involves only a few tasks that have to be handled carefully.
Set up your new hosting account
If you switch to a different hosting plan of the same web host, please skip this part. I assume most of you will switch to another host. You first need to purchase a new hosting plan and set it up before starting migration. Once you’ve set up your web hosting, you will be able to
- create a database
- install a new WordPress, and/or
- connect to the server using a command line interface.
I list these actions, because they involve important functions for managing your WP site. And the functions are sometimes disabled by default. You may be required to get your account verified to use them. Some American hosts ask you to make a phone call. It’s no problem for US citizens or someone living in the United States. But if you are/live outside North America, you may need to be ready in advance for the questions you will be asked. Most US hosts do not have international toll-free numbers; you’ve got to make an international phone call at your own expense. In my case, the verification call lasted almost 9 minutes. So it is a good idea to write down your hosting account, invoice number and other information before you make the call.
Export & Import your WP data
You can download your old WP data without any plugin. Login to your old WP Dashboard and move to Tools Export screen. The Export screen looks like this. When you click “Download Export File” on the screen, an XML file will be generated and downloaded to your computer. The file name should look like
YOUR_WP_SITE.wordpress.YYYY-MM-DD.xml
and contains your posts, pages, comments, custom fields, categories, and tags. In other words, it does not contain your Plugins and Settings. You need to manually install new plugins and adjust all the settings after importing your old WP data into the new website. The XML file does not contain your old WP theme files, either. They can be found under
YOUR_WP_ROOT/wp-content/themes/
on your old host so you can transfer the theme files from your old host to your computer and then from your computer to your new host using an FTP client. Now you have every content you can move and think about installing a WP onto your new host.
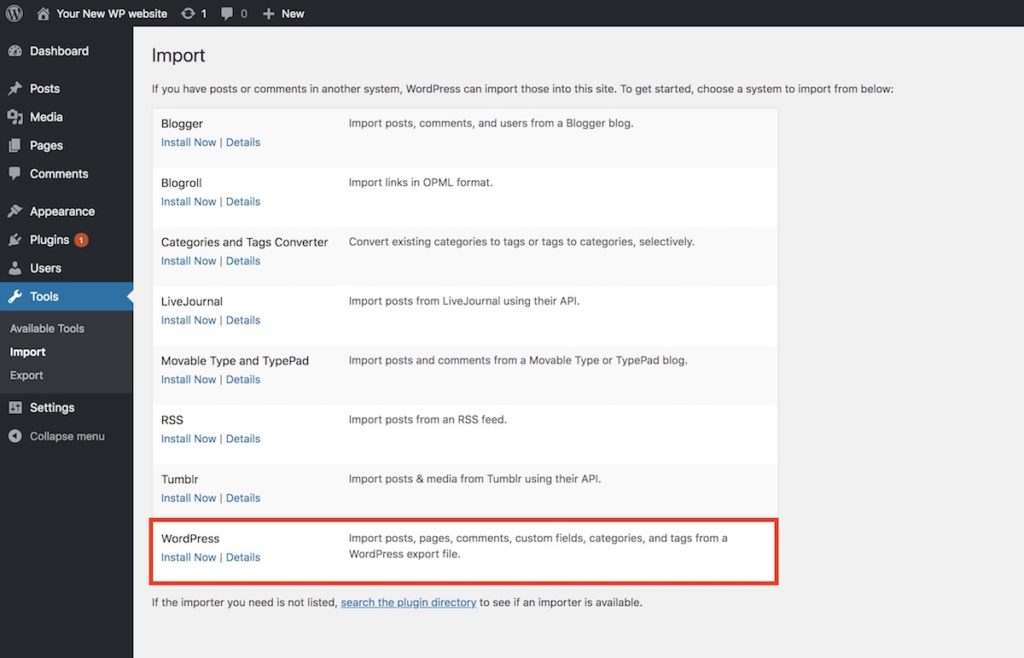
Go to your new host and install a new WP onto it. And login to the new WP site and move to Tools Import screen. The screen will list several system importers. Just click “Install Now” of the WordPress option.
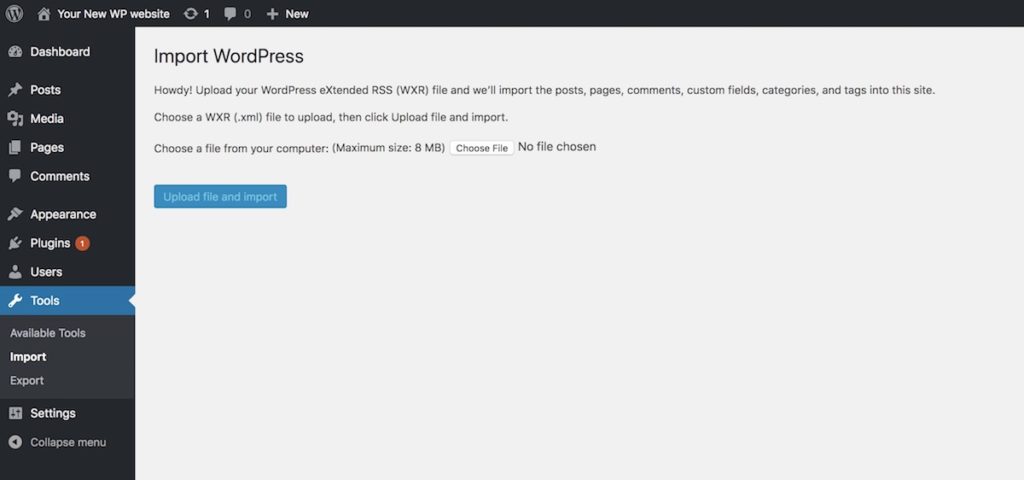
You will then be asked for choosing an XML file to upload. Press “Choose file” button, find the exported XML file and then hit “Upload file and import”.
Your old posts, pages, comments, etc. will be imported into your new WP site. Check and adjust your Permalinks, Plugins, Theme and other settings. It is also recommended to backup your new WP database at this point. You are going to edit the database. And if an unexpected error occur during editing, the WP will stop showing its entire posts and pages.
Edit your new WP database
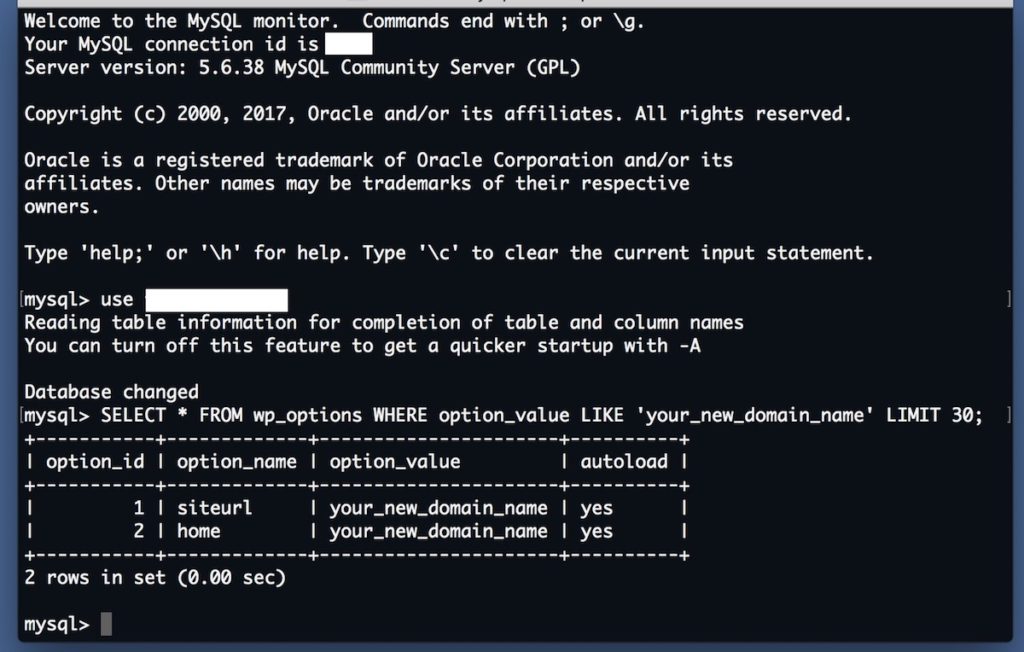
If your new WP site’s domain name is set to the previous one, please skip this part. Otherwise you need to edit your new WP database. Access the database using command line or phpMyAdmin. Select the “wp-options” table and find “siteurl” and then change “siteurl” option_value variable from the current one to the domain name of your old WP site. And then find “home” and assign the domain name to its option_value variable, too.
Once you succeed in editing the database, you will not be able to access your new WP site until you assign your domain to your new host. Keep that in mind.
Assign your domain to your new host
Login to your new hosting and find “Domains” section on the control panel. If you cannot find one, try using a search form. In the “Domains” section, you will most likely find “Assign” menu and be asked for the domain name that you would like to assign. Enter the domain name and change the nameservers for it. Once the nameservers are updated, all your Domain Name System (DNS) records for your domain will be overwritten to your new host. It may however take at most 24 – 48 hours to take effect. And your migration will be completed.